Electricity and Magnetism Collection
Welcome to the electricity and magnetism collection at Aberystwyth University Physics Museum. Here you will find a number of pieces of experimental equipment, previously used to explore the strange properties of electricity and magnetism.
This collection is split into seven sections:
- Arc Lamps
- Current Electricity
- Dynamo's and Motors
- Electrometers
- Electrostatics
- Galvanometers
- Magnetometers
ARC LAMPS
Jablochoff’s Candle
Circa 1895
Two carbon rods are used to suspend an arc of electricity. The carbon on this piece is broken.

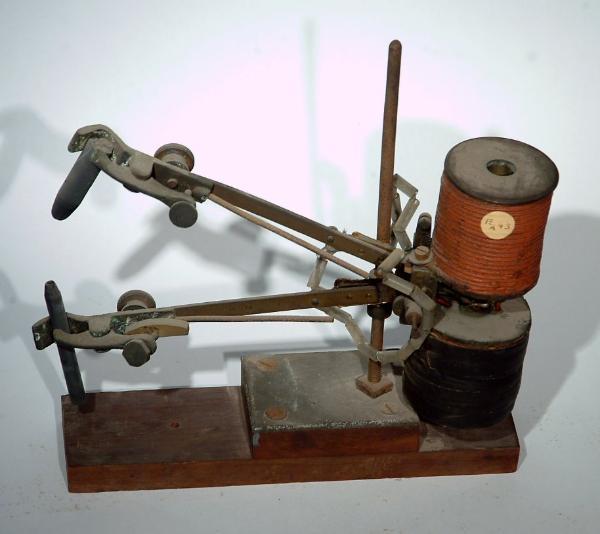
Scissor Type Automatic Arc
Circa 1900
A scissor-type automatic arc for a projection lantern. This piece appears to be home made from recycled materials.

CURRENT ELECTRICITY
Clorian Trydan Arglwydd Kelvin, "Patent Electric Balance" Rhif 70
Gan Kelvin and White Ltd. 1895
Fe'i defnyddid i fesur ceryntau D.C mawr. Mae'r cerrynt sy'n cael ei fesur yn cael ei roi drwy goiliau gwifrau paralel sy'n golygu bod mwy o gerrynt yn cael ei ddefnyddio o'i gymharu â'r gwifrau syth paralel. Mae'r grymoedd gwrthyrru rhwng y coiliau yn achosi i fàs bychan symud ar hyd dangosydd graddfa llorweddol. Mae'r pellter y mae'r màs yn cael ei symud yn gyfraneddol â sgwâr y cerrynt.

Electric Balance Apparatus
By Kelvin and White Ltd. 1895
A selection of weights and lenses for use with Lord Kelvin’s Patent Electric Balance.
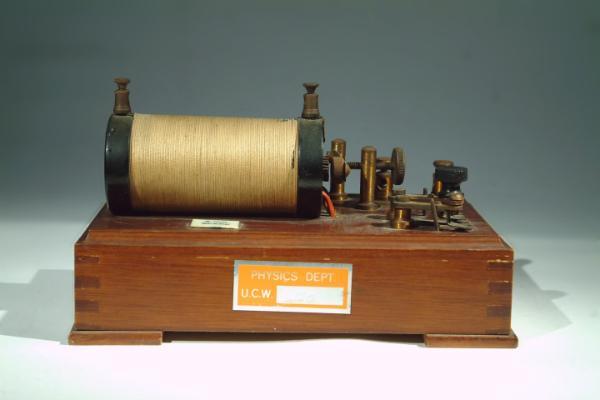
Induction Coil
Induction coils are transformers and are used generate a high voltage output current from a low voltage input. This piece has previously been used in the Physics Lab.

Dargludydd mewn Dirwyniad Stator
O Orsaf Trydan Dŵr Maentwrog. 1920.
Darn o fetel wedi'i labelu ‘Section of conductor in stator winding of 6,600 volt alternator at Maentwrog Hydro Electric Station'.
Pentwr Foltäig Sych
Tua 1890
Pentyrrau foltäig oedd y math cyntaf o fatris trydanol i gael eu defnyddio i ddarparu cerrynt parhaol i gylched drydanol. Mae hanner y pentwr ar goll.
Loaded Cable Paperweight
By B. Davies, 1910
A portion of loaded cable mounted as a paperweight. From the B. Davies collection.
Loaded Cable
By B. Davies, 1910
A portion of a loaded cable. From the B. Davies Collection.

Siemens Electrodynamometer No. 1670
By Siemens Bros. & Co. London. 1890
This is an early instrument for measuring power in both A.C and D.C. Two coils at right angles to each other have a current passed through them. This produces a torque which is dependent on the square of the current.
Wheatstone’s Bridge
By The American Electric Speciality Co., New York. 1899
Wheatstone’s bridge, otherwise known as a direct reading ohmmeter, is a piece of apparatus used to measure electrical resistance. These instruments are known for providing very accurate measurements.
Electrolysis of Water
Circa 1880
A device consisting of a glass vase with two electrodes, built to show the decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen. Likely used in lecture demonstrations.
Effects of Electric Current
Circa 1880
A coil with a balanced magnet, built for ‘demonstrating magnetic effects of a current’. Possibly used for lecture demonstrations.
Induction Coil
By Gebr Ruhstrat, Gottingen. 1900
Induction coils are transformers and are used generate a high voltage output current from a low voltage input.
Type BK24 Ignitron
By AEI.
Ignitrons are rectifiers that use a mercury cathode to be able to carry a large current. These devices are widely used in industry to convert large amounts of AC current to DC.
Vacuum Tube No. 555 80 Br 2
By Leybold-Heraeus.
This is a triode vacuum tube used to control the current between electrodes in a vacuum by a process call thermionic emission.
DYNAMOS AND MOTORS
D. C Dynamo
Circa 1895
A small early compound-wound dynamo with horse-shoe field magnet, rocking brushes and brass commutator.
Hand-Driven Demonstration Dynamo
Circa 1900
A dynamo with H-armature and horse-shoe field. This item was borrowed by B. Davies when living at Abermad during the years 1939-1945 and was used to charge an accumulator for use with a wireless receiver.
Model Electric Motor
This piece was used to demonstrate how an electric motor can power a pump. Purchased from St. David’s College, Lampeter, 1945.
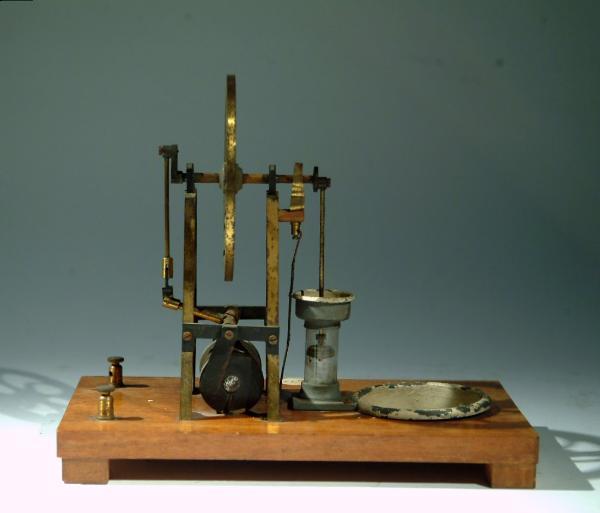

Gramme Machine
By U. C. W. Workshop. 1900
Gramme ring D. C motor with double horse field and rocking cooper gauze brushes. Appears to have been made in the Universities workshop.
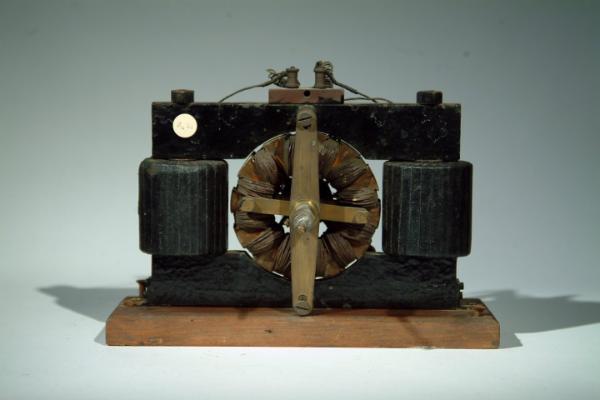

D. C Motor
By Cuttriss and Co. 1895
Similar in principal to a Gramme motor with an elaborate armature and rocking copper gauze brushes.
Model Electric Motor
Formerly the property of Prof. F. W. Rudler, this piece was used as a demonstration model for an electric motor.
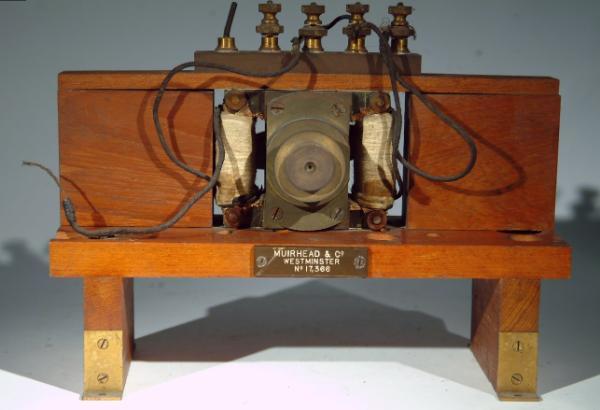
Demonstration Motor
By Muirhead and Co., Westminster. 1900
A demonstration motor for showing the characteristics of series and short circuits.

ELECTROMETERS
Electromedr Cwadrant
Gan W. G. Pye, Cambridge, 1930
Math Dolezalek o electromedr a fyddai'n cael ei ddefnyddio i fesur gwefr drydanol a'r gwahaniaeth potensial. Defnyddid yn y Labordy Anrhydedd hyd at 1955.


Electromedr Cwadrant Cynnar mewn Cas
Gan Elliot Bros. London. 1890.
Fersiwn gynnar o electromedr cwadrant a ddefnyddid i fesur cerrynt a gwahaniaeth potensial. Mewn cas, wedi'i orchuddio gan gysgodlen wydr â leinin ffoil-tun.


Quadrant Electrometer
By J. White, Glasgow, 1890
A quadrant electrometer of the Kelvin type, with a small electrostatic machine and concentrated sulphuric acid (H2SO4) to keep the humidity inside the electrometer low.
ELECTROSTATICS
Electrosgop Dalenni Arian

Defnyddir yr offer i ddangos anwytho electrostatig ac i brofi'r wefr ar wrthrych. Os yw'r gwrthrych dan sylw wedi'i wefru, bydd y dalenni arian yn gwrthyrru a symud oddi wrth ei gilydd pan fydd y gwrthrych yn mynd tuag at y ddisg.
Electroscope
By Harvey and Peak.
This electroscope works similar to the one above. The metal plate on the glass rod is charged and is brought close to the plate that's connected to the silver leave, this causes the leaves to repel.
Eitemau ar gyfer Electrosgop Pêl-fywyn
Tau 1900
Detholiad o eitemau i ddangos anwytho electrostatig ar electrosgop pêl-fywyn.
Jar Leiden
Tua 1890
Defnyddir jariau Leiden i gadw trydan statig rhwng dau electrod, er mwyn dangos bod "egni yn aros mewn deuelectrynnau”.
Peiriant Voss
Gan F. E. Becker. 1870.
Cyfarpar anwytho electrostatig lle mae deuelectryn ynysedig yn cael ei wefru ac yn anwytho gwefr ddirgroes ar ddargludydd ynysedig. Mae'r handlen yrru a'r pwli ar goll. Prynwyd oddi wrth Goleg Dewi Sant, Llanbedr Pont Steffan, 1944.
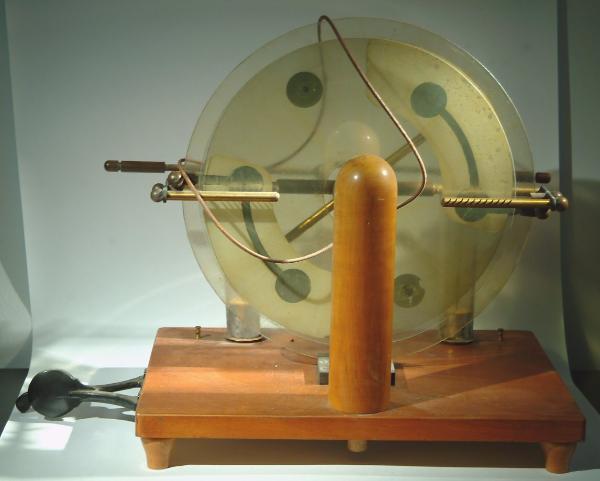

Peiriant Silindr Gwydr Electrostatig
Gan William and Samuel Jones, No.135 Holborn, Llundain. 1790.
Darn mawr o offer a wnaed gan y brodyr enwog yn Llundain. Mae'r darn hwn yn cynnwys stand, clychau trydanol, electrosgop cwadrant, gwallt a gefeiliau dadwefru.
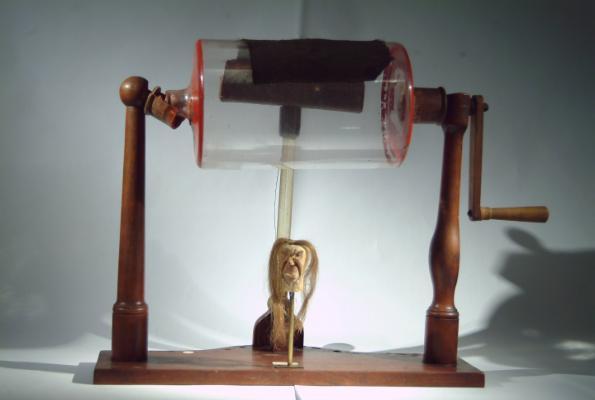

Clorian Ddirdro Coulomb
Tua 1890
Fe'i defnyddid i fesur grymoedd gwan fel y grym electrostatig rhwng gwefrau. Dyma a ddefnyddiwyd gan Coulomb i brofi Deddf Coulombs.
Ayrton-Mather Electrostatic Voltmeter
By Robt. W. Paul, London.
This voltmeter is similar to a quadrant electrometer and uses a beam of light, reflected off a mirror as its needle. It could measure AC and DC voltages up to 10 Volts.
GALVANOMETERS
Galfanomedr Drych Thompson
Gan W. Thompson. 1858.
Fe'i datblygwyd i fesur amrywiadau yn y cerrynt mewn ceblau hir. Mae drych bach, â magnet wrth ei gefn, yn cael ei roi ynghrog mewn poced o aer o fewn coil hir o gopr. Mae golau'n cael ei ddisgleirio ar y drych a'i adlewyrchu ar sgrin neu ddangosydd graddfa. Pan fydd cerrynt yn mynd drwy'r coil, ac yn anwytho maes magnetig, mae'r drych yn cylchdroi yn ôl cryfder y cerrynt. Gellir gweld yr allwyriad [deflection] wedyn ar y sgrin.
Galfanomedr Adlewyrchol â Magnet Symud
Gwnaed yng Ngweithdy'r Coleg. 1900.
Galfanomedr i ganfod ceryntau a'u mesur, gyda darpariaeth ar gyfer llafn gwanychu.
Darnau Galfanomedr
Amryw ddarnau ar gyfer galfanomedr. O gasgliad B. Davies.
Tangent Galvanometer No. 5657
By W. G. Pye.
This is a sensitive galvanometer. It is set-up with the needle pointing magnetic north-south and parallel with the coil. When a current is passed through the coil, the magnetic field produced causes the needle to deflect. The tangent of this angle is then proportional to the current in the coil.
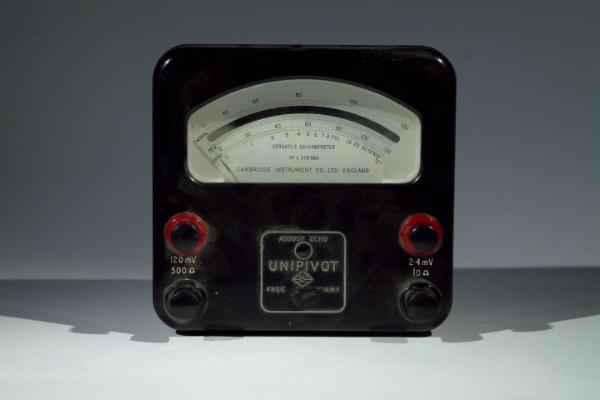
Unipivot Versatile Galvanometer No. L318966
By Cambridge Instrument Co. Ltd.
Unipivot galvanometers were a step-up from the traditional moving coil designs. Here the circular oil is pivoted on a spike about its centre of gravity, such that movements to not disturb the needle.

Reflecting Moving-magnet Galvanometer
By Nalder Bros., 1900
A small galvanometer by Nalder. Missing some parts.
Reflecting Astatic Galvanometer
Circa 1900
A reflecting astatic galvanometer with no markings. From the B. Davies collection.
Moving Magnet Reflecting Galvanometer
By Cambridge Scientific Instrument Co., 1890
A moving magnet reflecting galvanometer with a 2 ft. long suspension and elaborate adjustments.
Broca Galvanometers
By Cambridge Instrument Co., 1910
An Astatic type, Broca galvanometer, there are two in the collection.
D'Arsonval-Deprez Galvanometer
By T. Carpentier, Paris, 1890
This galvanometer design allows the scale to be linear as the current through the coil is proportional to its angular deflection. The glass case is damaged.
Astatic Galvanometer
By Horne & Thornthwaite.
Astatic galvanometers were more accurate than previous designs as they eliminated the effect that the Earth’s magnetic field had on the galvanometers needle.
Mirror Galvanometer
By Gambrell Bros.
This piece was previously used in the Physics Lab. It is quite an elaborate design and may have been used to carry out very precise measurements.
Mirror Galvanometer
By Gambrell Bros.
This piece was previously used in the Physics Lab. It is quite an elaborate design and may have been used to carry out very precise measurements. Glass screen is chipped and damaged.
Moving-Coil Galvanometer
By Hartmann and Braun, Frankfurt, 1910
This is a very sensitive instrument for the measuring of small currents of the order of 10-9 Amps. This piece allows weights to be added to adjust the sensitivity.
Galfanomedr Astatig mewn Cas
Gan Elliott Bros. 1900.
Galfanomedr astatig gyda siyntiau. Mae hyn yn well na'r galfanomedr syml gan ei fod wedi cael gwared ag effaith maes magnetig y Ddaear ar y nodwydd. O gasgliad B. Davies.
Ayrton-Mather Galvanometer
By Robt. W. Paul, London, 1920
This is an extremely sensitive instrument due to the shape of the coil giving it a low moment of inertia. This galvanometer comes complete with case.
Moving-Coil Galvanometer with Electromagnetic Field
By E. D., U. C. W. Physics Lab, 1900
This galvanometer was produced by Aberystwyth University Physics Lab around 1900. It is marked E. D on the bottom.
Campbell Vibration Galvanometer
By Robt. W. Paul, London, 1920
In this piece of apparatus, the mirror is suspended by a vibrating wire, which is then tuned to a resonance frequency. When the current is applied, the wire deflects and the mirror moves. The string vibration allows this instrument to be very sensitive.
DC Range Box
By Cambridge Instrument Co.
DC range box for versatile galvanometer originally designed for use with a 500 Ohm Unipivot galvanometer. Previously used in the Honours Lab.
Admiralty Pattern 5946 Integrator A/S 91
By R. B. Pullin. 1939
This piece houses a suspension galvanometer for the detection of submarines and in oceanographic work.
MAGNETOMETERS
Magnetomedr Adlewyrchu â Magnet Symud
Gan W. Groves, Llundain.
Cyfarpar manwl-gywir ar gyfer mesur cerrynt trydanol. Pan gyflwynir cerrynt trydan i'r coil magnetig, mae'r maes magnetig a anwythir yn achosi i'r magnet, sydd wrth gefn y drych, allwyro a chylchdroi yn ôl maint y cerrynt. Pan adlewyrchir goleui oddi ar y drych, fe ellir gweld yr allwyriad sy'n digwydd oherwydd y cerrynt, a'i fesur.
Magnetomedr Allwyriad
Gan Hartmann and Braun, Frankfurt. 1910.
Cyfarpar a ddefnyddid i fesur magneteiddio, cryfder, cyfeiriad a newid maes magnetig mewn deunydd magnetig. Mae'r cyfarpar hwn yn cynnwys gwanychu magnetig.

